Investment Strategies
The Rise Of Digital Health And Genomics In Europe
Terms such as genomics, telemedicine and healthtech are increasingly parts of the investment vocabulary. The long-term nature of such areas makes them well-suited to the wealth management audience. This article delves into the details.
In this commentary from thematic investing firm Global X (more details below) it explores the ways in which forces such as ageing, modern science and technology have come to together to change healthcare and, with it, investment opportunities in the space.
The article is by Morgane Delledonne, director of research, Global X. The editors of this news service are pleased to share these insights and invite responses. The usual editorial disclaimers apply to views of guest contributors. To respond, email tom.burroughes@wealthbriefing.com and jackie.bennion@clearviewpublishing.com
Structural trends such as inequality, ageing populations,
systemic inefficiencies, and improving connectivity have
reinforced the need for the adoption of technology in the
healthcare sector. While the healthcare sector was slow to
embrace the digital transformation offered by emerging
technologies for many years, the pandemic has been a catalyst to
the adoption of telemedicine and digital health globally. The
overall digital health market is expected to grow from $216
billion in 2020 to more than $657 billion by 2026. In the
following piece, we explore the digitisation of healthcare in
Europe and the telemedicine, digital health, and genomics
companies leading in the region.(1)
Intergovernmental initiatives drive the digitisation of
European healthcare
European countries face several health-related challenges,
including ageing populations, chronic diseases, unequal quality
and access to healthcare services, and a shortage of health
professionals. In Europe, digital health emerged as a strategic
health priority well before the COVID-19 pandemic, but the crisis
further accelerated its adoption across the block.
Prior to the pandemic, Horizon 2020 was the largest EU research
and innovation programme with nearly €80 billion of funding
available over 2014 to 2020 (2). Among other innovative projects,
Horizon 2020 funded Digital Health Europe, which is aimed at
supporting large-scale adoption of digital solutions for
person-centred integrated care, promoting digitised models of
care, enabling breakthroughs and securing Europe's global
competitiveness. For example, Digital Health Europe funded a
project in Spain and Portugal that has created an artificial
intelligence (AI) system capable of monitoring and predicting
future relapses of patients suffering from multi-morbidity
conditions (3). In 2019, the World Health Organisation (WHO) and
the European Union (EU) advocated the use of health technologies
to reduce inequalities and improve health and wellbeing (4). Both
organisations emphasised digital health as a crucial component of
healthcare services to actively contribute to the achievement of
the United Nation’s Agenda 2030 Sustainable Development
Goals.
Since the COVID-19 pandemic began, public authorities have
increasingly relied on the use of digital solutions such as
telemedicine and contact tracing apps to facilitate virtual
patient-doctor visits and monitor outbreaks. As the world returns
to normal, Europe is building on the recent momentum to continue
to digitalise healthcare across the region. The European
Programme of Work for 2020–2025, called “United Action for Better
Health” sets priorities for the future of healthcare in Europe
and identifies digital health as key to realising this vision.
The EU has also created EU4Health, investing €5.1 billion, to
continue efforts from the Horizon 2020 programme (5). The main
objectives behind digitisation of healthcare are to secure access
and exchange of health data across the EU, and pool health data
for research and personalised medicine. These initiatives will
spur existing efforts to adopt digital health across Europe and
complement the WHO Global Strategy on Digital Health.
European digital health and genomics markets
Telemedicine, digital health and genomics companies posted strong
performances amid the pandemic, given the sector's defensive
nature and a surge in healthcare-related spending to combat
COVID-19. The MSCI World Health Care Index and the Solactive
Genomics Index increased 12 per cent and 52 per cent respectively
in 2020. The digital health market in Europe was valued at $38.1
billion in 2019 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.1 per
cent over the next five years (6).
Telemedicine and digital health
The European market for healthcare information technology (HCIT)
and related services, is growing substantially, spurred by the
expanding volume of data in healthcare, the need for fast and
efficient processes and patients’ growing need for data
accessibility. The COVID-19-pandemic in 2020 and the immense
stress it has put on the European healthcare system have
accelerated demand for HCIT solutions. This growth trend has also
been powered by public financial initiatives in recent
years.
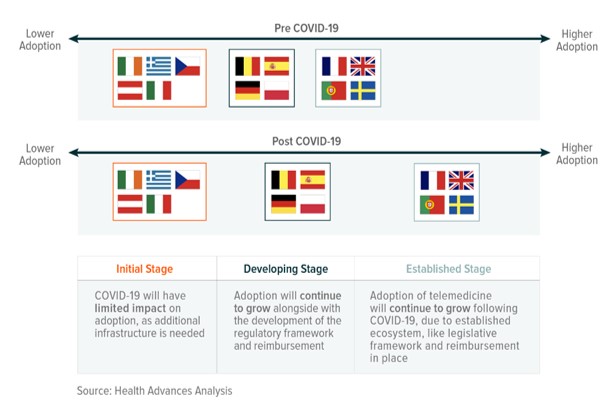
COVID-19 impact on telemedicine adoption in EU
countries
Telemedicine accounted for $1.7 billion in 2019 and is expected
to be the fastest growing segment of the European digital health
market with a CAGR of 26.1 per cent over the next five
years (7).
One of the main companies in the digital health sector is Compugroup Medical SE (CGM), a Germany-based top provider focusing on software solutions for health professionals. Its activities are divided into Health Provider Services, focusing on the development and sale of software solutions for professional healthcare settings and Health Connectivity Services, a networking service between participants in the healthcare sector. The CGM group is successfully converting its product portfolio to a Software-as-a-Service model, becoming a leading player in the development of global eHealth solutions. CGM expects revenue growth of 19 per cent in 2020 to rise to 24 per cent in 2021, including two acquisitions completed in the financial year 2020. Organic growth is expected to range between 4 and 8 per cent (8).
Genomics
Since the completion of the Human Genome Project in 2003,
genomics research has accelerated alongside the vast collection
of genetic data across populations.
By developing a greater understanding of the human body at a
genetic level, new therapies are emerging that can treat diseases
that were previously considered uncurable. Going forward,
integrating data from several genomics-based research projects
and data sets will require a greater incorporation of computing
technology, such as AI-driven computational biology in the drug
development process. Moreover, we believe that AI-based drug
development is likely to benefit from the continued digitisation
of personal biological data and electronic health
records.
The growth of the genomics market has largely been driven by
factors such as availability of government funding, the
collection of genetic data, the number and success of
genomics-based studies, disease rates, technological
advancements, demand for modified crops, and discoveries of
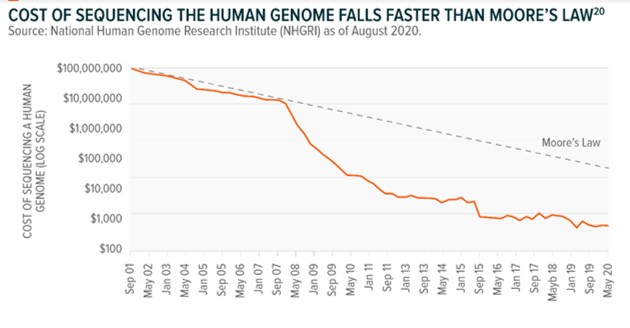
new-use cases for genomics-based treatments. As DNA sequencing
costs continue to fall at a rapid rate, the collection of genetic
data is becoming easier, furthering advancements in the genomics
space (9).
Good examples of the rapid growth of the genomic market are
uniQure NV, a Netherlands-based company focusing on the
development of gene therapies and Cellectis SA, a French company
which is active in the field of gene-editing. Gene therapy seeks
to modify or control how one’s body expresses certain genetic
information, potentially replacing, modifying, or deactivating
the genes associated with debilitating diseases. Year-on-year
uniQure NV grew revenues by 415.2 per cent from $7.28 million to
$37.5 million (10).
Cellectis develops off-the-shelf gene-edited CAR-T cells that aim
to force the immune system to target and eradicate cancer cells.
Year-on-year Cellectis SA grew revenues by 258.7 per cent from
€23 million to €82.5 million (11).
Conclusion
Telemedicine and digital health can expand access to healthcare
by making it more geographically and financially accessible,
presenting opportunities for large-scale adoption in Europe and
around the world. In the meantime, genomics can revolutionise
treatment options and improve patient outcomes with the rise of
personalised medicine. We believe that the benefits seen by
patients, providers, and payers will continue to drive the
overall adoption of these themes.
Global X, the New York-based firm, operates in the field of thematic investing, providing exchange-traded funds and other investment entities. It oversees more than $33 billion in assets across more than 80 ETF strategies.